Terminology
Persistent cookie — A cookie that remains present in the visitor’s web browser and that contains the identification of the visitor which allows the system to recognize the visitor at later visits.
First-party cookie — First-party cookies are cookies set with the same domain as in the browser’s web address.(Example: when browsing http://www.parana.com website, a first-party cookie has the same domain reference parana.com)
Third-party cookies — Third-party cookies are set with a different domain than the one shown in the address bar.
A visit in Site is a period of time in which the visitor is active. Whenever the visitor hits your website, a tracking call will be fired to Site on which the profile will be updated. When hitting an existing profile, Site will check the difference between the current time and the time of the previous hit on the profile. If the difference (in minutes) between these 2 times is more than the configured threshold, Site will consider the tracking call as a new visit. When it is less than the threshold, it is considered the same visit.
Example: The threshold is set to 30min.
The visitor opens your website in a browser.
The visitor clicks around a few times hitting a certain profile.
10 minutes later, the contact returns to your website in the same browser
Within this scenario, NO NEW VISIT is generated since the time between the 2 sessions was less than 30 minutes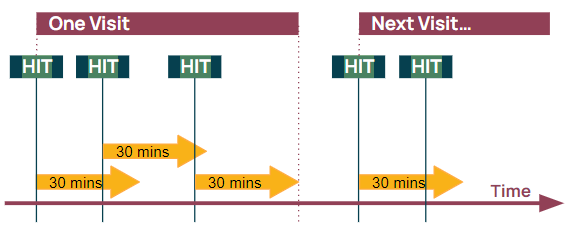
All pages with the Sitetracking script included will generate a ‘hit’. This is all page views but also every time you send JavaScript values back to Siteon page load (view) or on a click (event).
One universe is linked to one Engage environment. But 1 Engage environment can have multiple universes linked to it, each universe using a different Audience List.
Technical note:
Although it is possible to have multiple universes linked to the same Engage environment and Audience List, it doesn't really make sense to do this as data will be shared and stored in the same Audience List anyway. One example of a possible setup could be when using a production website and a testing website in 2 separate universes and 2 separate organizations sharing the same Audience List. People testing offers in the staging environment can then use 'live' data from the shared Audience List.:
(By default Site allows one universe to be created. If more universes are required, contact Marigold.)
Tags are used to identify the pages/products that are visited by assigning these pages/products a specific tag and a value. These tags get a score that is updated at each visit. The value can either be:
- textual (example: Phones, Video, Computer)
- numeric (the price, a bonus point, etc).
- Textual tags can have a hierarchy.
Hierarchical tags — Textual tags that contain and include a hierarchy, often representing the hierarchy of the website itself. Hierarchical levels can go 5 levels down. The values per level are separated by an underscore. Example: Tag: Clothing with value Women_Clothes_Dresses.
Reporting segments — Reporting segments contain profiles answering specific Reporting segment constraints. When new profiles come online they are evaluated at every click to determine the Reporting segment to which they belong. Reporting segments are created for reporting purposes and are calculated once a day.
Placements (placeholders) indicate where content for offers should be placed on the website, such as banners, html, pop-ins, pop-ups, etc. The content itself is not defined in a placement itself, this is done in the offer.
Based on the visitor’s website behavior, Offers in site allow you to show content specifically for them. You can create an audience for your offer, set goals and measure conversions. Follow-up or retarget with Engage journeys. Offers can be scheduled and goals can be defined and measured to obtain funnel reports. An offer consists of one or more actions.
Actions — An action indicates the actual content that should be displayed in the placement and how it should be displayed.
A conversion happens when the Offer has reached its goal. For instance, if your offer stimulates a second purchase, evidently the visitor is converted when the number of purchases is 2. Or, when the offer is about adding visitors to a loyalty program, conversion happens when the visitor joins the program.
A pop-in is a piece of content that is displayed within the current website page. It does not block the visitor from navigating the website and is less intrusive than a pop-up message which opens in a new window blocking any further navigation from the visitor.
Recency (decrease) — This is a tag reporting setting. The amount of time a value is valid. For instance, the number of purchase will not decrease in time. Your first purchase will always be your first purchase. While others, like a visit to the Electro products overview page, most likely isn't valid forever. Perhaps even only for 1 day.
Frequency capping is a technique in Site to limit the number of times a placement can be used. A placement can be set as interruptive and in that case you want to limit the number of times this changes. This limitation is set on universe level
Example: An image in the header of the website can only be changed once a week. This limitation is set on universe level .
Capping is a technique used in Site, to limit the number of times an offer will be shown to a visitor.
- Action capping - limited at Offer action level
- Offer capping - limited on Offer level and affects all actions in the offer
- Placement frequency capping - defined on Placement level and affects all offers that use that placement
Example: Only show this offer once per visit.
DMP — Data Management platform
A profile is the representation of an individual visitor. For each visitor information is stored in their profile and updated with each visit. If they visit the website through a Engage email, they are recognized as a Engage contact user and are “CRM identified”. If they log in on the website and their unique identifier is sent to Site, they are “custom identified”. If they log in on different devices (pc, tablet), or opens the email on different devices, the information of the visitor is grouped in one single profile.
Active profiles are profiles of visitors for whom activity(a view, a click or any mouse or keyboard activity) was registered on the website for the last x days/weeks/months. The time span is defined in the properties of the universe itself.
|
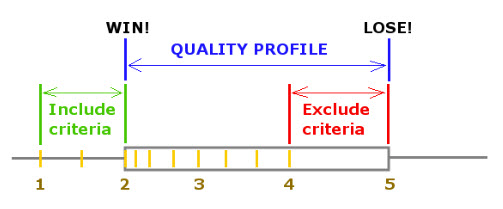
A quality profile is a profile that answers the qualifying include and exclude criteria defined on universe level. Only qualified profiles are stored. If they do not reach the criteria; the criteria that they did reach (e.g. 2 hits) are stored in a persistent cookie on the visitor's computer. Otherwise Sitewould not know when to start building profiles. |
|
Win/loss is used in relation to profiles.
'Win' represents a new profile that answers the include criteria defined in the universe settings. This also includes old profiles that have been lost but that come back online and answer the include criteria. These profiles are also referred to as Quality profiles/
'Lost' refers to profiles that answer the exclude criteria defined in the universe settings.
A Consentless visitor is a visitor that refuses cookies and can therefore not be tracked. Every hit is considered as a new visit and anonymous. Consentless visitors can be targeted with contextual offers (offers that are pushed depending on the page they are on, the time of day, etc) through Site but they cannot be messaged via Engage (no email, SMS, mobile message).
Example: A customer enters a bar and the barman turns to the new customer and says 'hi welcome, what can i get you'. When the customer leaves his seat to hang his coat and comes back, the barman turns around and says 'hi, welcome, what can i get you'. To the barman, this is again a new customer.
An Anonymous visitor is a visitor that accepts cookies and as a result every hit is tracked. These visitors are not known yet (not identified) but we do know their behavior and they can be targeted with offers through Sitebut not messaged via Engage.
Example: A customer sits at the bar and orders a drink. When he leaves his seat to hang up his coat and comes back to the bar, the barman turns to the customer and asks 'you want the same?'.
When the customer leaves the bar and forgets a coat, the barman has no way of contacting the customer.
A Custom Identified visitor is a visitor that accepts cookies and as a result every hit is tracked. These visitors can be targeted with offers via Site but not messaged via Engage. These visitors are known to the website and Site but they are not known in Engage.
A CRM-identified visitor is a visitor that accepts cookies and as a result every hit is tracked. These visitors can be targeted with offers through Siteand messaged via Engage. They are known to the website, Siteand Engage.