With the Time component you can decide when an email should be sent (for data driven journeys). Or which route the contact takes in the journey, based on the time condition set in the Time component.
Send an email in a data driven (scheduled) journey only between working hours.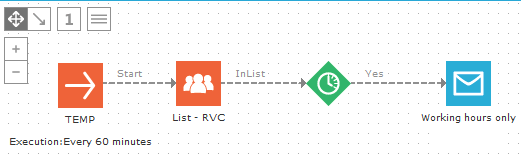
If the contact clicks "Submit" on weekdays, he will see a different page then in the weekends.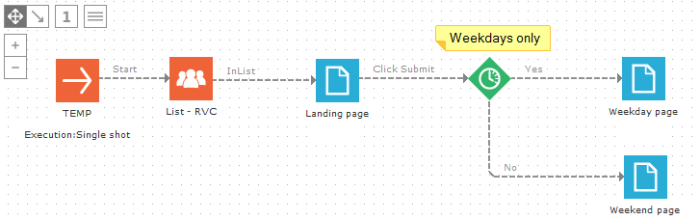
The Time component is of no use in a single shot journey. The single shot journey is executed once, when it is launched. You can set a launch date in the journey properties.
Events
The time component triggers two types of events:
- OnYes: the current time matches the defined condition.
- OnNo: the current time does not match the defined condition.
Properties
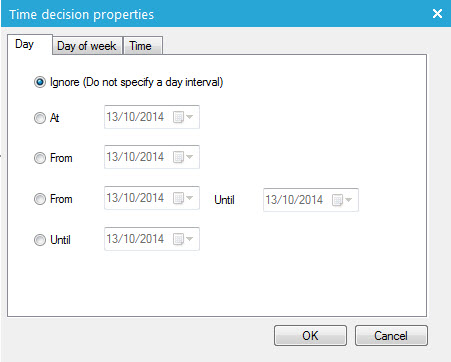
Day
Use this tab to define a specific date at which action must be taken.
If no action must be taken at a specific date, flag the option ‘Ignore’. Else, select one of the following options:
- At: select the exact date on which action must be taken.
- From: select the exact date from which on action must be taken
- From – Until : select a time interval between two dates to take action
- Until: select a date to stop taking action
Day of week
In addition to a specified date, it is possible to define one or more days of the week to take action.
If no specific day must be defined, leave the option ‘Ignore’ checked. Else, flag the option ‘At’ and select the different days of the week on which action must be taken.
Time
Specify a time for the action to be taken. The options are comparable with the day options.
Select a time for the action to take place or ignore this by selecting the first option.
- At: the exact time at which action is taken.
- From: the time from which action starts
- From – Until : the time interval in between which action is taken
- Until: the exact time to stop taking action
For 'Time', 'At' is rarely a good choice. This means that the contact must pass the Time component at that exact moment. Or that a data driven journey is executed at that exact moment. Which is highly unlikely. If this is not the case, the 'No' event will trigger.
